What Are Shin Splints?
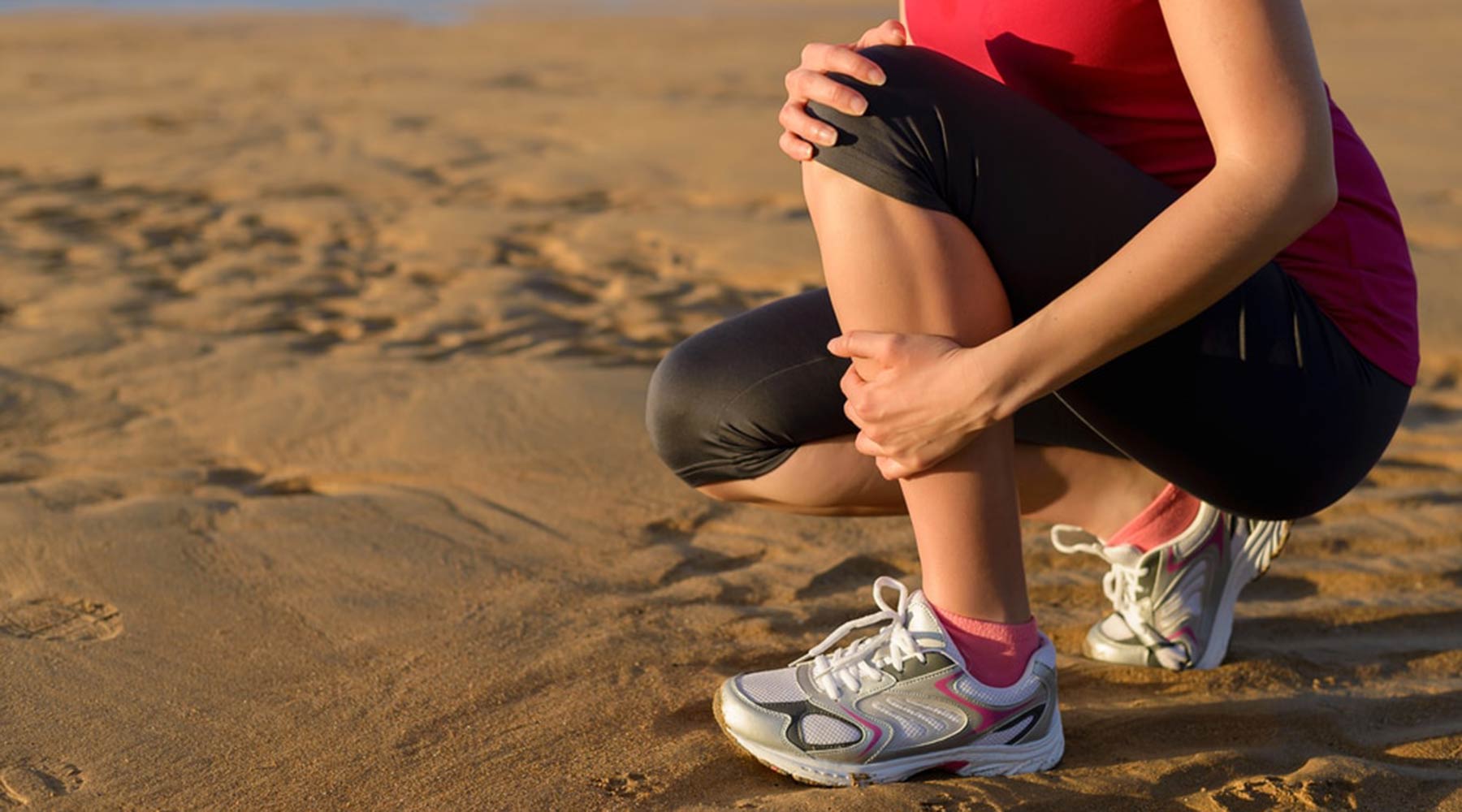
Shin splints, or medial tibial stress syndrome (MTSS), are a frequent issue among runners, dancers, and athletes involved in high-impact activities. This condition involves inflammation and pain around the shinbone (tibia) due to overuse.
The discomfort often presents as a dull ache along the inner shin and can become more intense with activity, sometimes leading to swelling or tenderness. If not addressed properly, shin splints can escalate into more serious issues like stress fractures.
Causes And Symptoms of Shin Splints
Shin splints can result from several factors. These include overuse or a sudden increase in training intensity, running on hard or uneven surfaces, and wearing improper footwear that lacks adequate arch support. Muscle imbalances or weaknesses and biomechanical issues such as overpronation or high arches can also contribute to the condition.
The primary symptoms are a dull pain along the shinbone, tenderness or swelling in the affected area, pain that worsens with activity, and difficulty bearing weight on the leg.
Differentiating Shin Splints from Stress Fractures
It’s important to distinguish between shin splints and stress fractures. Unlike shin splints, stress fractures involve an actual crack or break in the shinbone, resulting in sharp, localised pain that typically worsens with weight-bearing activities.
Stress fractures require prompt medical attention and a longer recovery period compared to shin splints.
The Importance of Proper Footwear in Preventing Shin Splints
Wearing appropriate footwear is crucial for preventing shin splints. Shoes that offer good cushioning, arch support, and a proper fit can help distribute impact forces and reduce stress on the lower legs.
It is essential to replace worn-out shoes regularly, as continued use of unsupportive footwear can increase the risk of developing shin splints.
Support Insoles for Shin Splints
Insoles can provide additional support and cushioning to alleviate shin splint pain. Arch support insoles help distribute weight evenly and reduce strain on the shins, while cushioned insoles offer extra shock absorption.
Motion control insoles are designed to address excessive pronation or supination, which can contribute to shin splint development. Choosing the right insoles depends on your foot type and activity level, and it may be helpful to consult a podiatrist for the best options.
Effective Treatment Strategies for Shin Splints
To treat shin splints effectively, start by resting and applying ice to the affected area to reduce inflammation and pain. Using compression sleeves or wraps can provide additional support and reduce swelling.
Elevating the legs above heart level when resting promotes blood flow and further reduces swelling. Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help alleviate pain and inflammation.
Incorporating stretching and strengthening exercises into your routine improves flexibility and strengthens the muscles around the shins, which can help prevent future episodes.
Physical Therapy Exercises for Shin Splint Relief
Specific physical therapy exercises can help relieve shin splint pain and prevent recurrence. For instance, calf raises, where you stand on your toes and then lower back down, strengthen the calf muscles and reduce strain on the shins.
Toe raises, performed by lifting your toes while keeping your heels on the ground, target the front muscles of the lower leg. Heel walks involve walking on your heels to strengthen the front lower leg muscles and improve ankle flexibility.
Foam rolling the lower leg muscles, including the calves, shins, and Achilles tendon, helps release tension. Incorporating stretches for the calves, hamstrings, and Achilles tendon into your routine can also improve flexibility and reduce strain on the shins.
It’s beneficial to consult a physical therapist to ensure these exercises are performed correctly and are tailored to your specific needs.
Tips for Preventing Shin Splints During Exercise
To prevent shin splints, it is important to warm up properly with light cardio and dynamic stretches before engaging in high-impact activities. Cooling down with static stretches and light walking afterward is also crucial.
Gradually increasing the intensity, duration, and frequency of exercise allows your body to adapt and reduces the risk of injury. Incorporating low-impact activities like swimming or cycling into your routine provides a break from the repetitive stress of high-impact exercises.
Strengthening your core and lower body helps absorb impact and reduce strain on the shins. Varying your running surfaces between softer options like grass or trails and harder surfaces like concrete can also help prevent shin splints.
Always listen to your body; if you experience persistent pain or discomfort, take a break and allow for recovery.
How to Manage Shin Splint Pain While Continuing to Exercise
If you wish to continue exercising while managing shin splint pain, focus on low-impact cross-training activities such as swimming, cycling, or using an elliptical machine to maintain cardiovascular fitness while reducing stress on your shins.
Modify your exercise routine by decreasing the intensity, duration, or frequency of high-impact activities until your shin splints have healed. Ensure you wear supportive, well-cushioned shoes and consider using insoles designed for shin splint relief to minimise impact on your lower legs.
Applying ice and compression before and after exercise can help manage pain and inflammation. Incorporating targeted stretching and strengthening exercises into your routine can aid in healing and prevent further injury.
Pay attention to your body’s signals; if pain persists or worsens, it’s crucial to take a break and allow for full recovery.
When To See a Doctor for Shin Splints
Most shin splint cases can be managed with self-care and proper rest. However, if the pain continues or worsens despite these efforts, or if significant swelling, bruising, or difficulty bearing weight occurs, it may indicate a more serious injury requiring medical evaluation.
Additional signs that warrant a doctor's visit include fever or redness around the affected area, which could signal an infection, or recurrent shin splints despite following treatment and prevention strategies. Consulting a sports medicine professional can provide an accurate diagnosis and a tailored treatment plan to prevent further complications.
Taking Care of your Shins with Lightfeet for Long-Term Health
Managing shin splints effectively involves a combination of proper treatment, prevention, and ongoing care. By incorporating appropriate footwear, supportive insoles, targeted exercises, and a gradual approach to training, you can alleviate shin splint pain and reduce the risk of future issues.
Prioritising rest and recovery is crucial for a successful return to your activities.
The two most common reasons for shin splints are overtraining and worn-out footwear.
If you want to avoid shin splints, it’s a good idea to prepare your muscles with warm-up exercises before you work out. If you’re trying something new (i.e. moving from running on a path to beach runs, playing more netball than usual and so on) then build up to it over time while your muscles get stronger! And in-between workouts, allow time for sufficient rest and recovery – include some stretching, strengthening exercises and massage.
Finally, make sure you have good gear; think our supportive insoles, the Lightfeet Support Insole, and sneakers that aren’t worn out.
NOTE: If you are experiencing persistent pain or discomfort, it is recommended to seek professional medical advice for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.